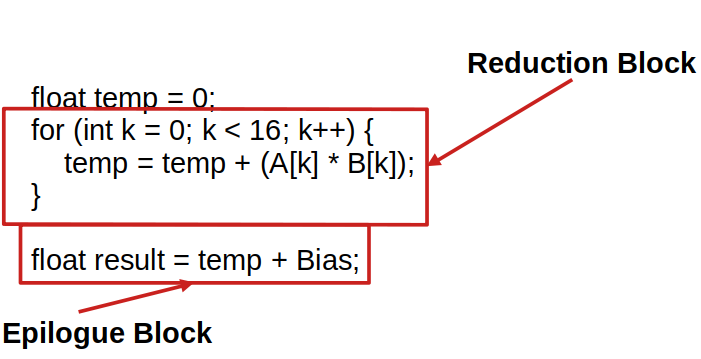
[TIR][Schedule] FuseReductionEpilogue: Expression-Based Generalization
Published:
Overview
The previous implementation of fuseReductionEpilogue relied on explicit pattern matching. Each epilogue type (Bias, BiasReLU, Clipping) required its own dedicated code path. While this worked functionally, it had several limitations: adding a new activation function required touching the core logic, and every new pattern needed explicit handling code.
We generalized fuse_reduction_epilogue so that it can handle arbitrary epilogue expressions without explicit pattern matching.
Pattern-Matching-Based Design
In the pattern-matching-based design, we used an EpilogueType enum and analyzed patterns case by case.
enum class EpilogueType { Bias, BiasReLU, Clipping };
bool AnalyzeEpiloguePattern(const PrimExpr& value) {
if (const auto* add = value.as<AddNode>()) {
// Detect Bias pattern: temp + C
return EpilogueType::Bias;
}
if (const auto* max_node = value.as<MaxNode>()) {
// Detect BiasReLU pattern: max(temp + C, 0)
return EpilogueType::BiasReLU;
}
// ... more pattern-matching cases
}
This led to code like the following:
if (epilogue_type_ == EpilogueType::Bias) {
// Bias-specific handling
} else if (epilogue_type_ == EpilogueType::BiasReLU) {
// BiasReLU-specific handling
} else {
// Clipping-specific handling
}
Expression-Based Generalization
Epilogue fusion follows a consistent mathematical structure.
In the Init transformation, we replace the reduction buffer load with the identity element (0 for addition). In the Update transformation, we replace the reduction buffer load with the reduction update expression, while properly handling the addend.
The target flow is as follows:
flowchart TD
A[fuse_reduction_epilogue call] --> B[BodyPatternAllowFusion]
B --> C{Is epilogue body<br/>a BufferStore?}
C -->|No| REJECT1[Reject: BodyAnalysisError]
C -->|Yes| D[Check # of reduction buffer uses<br/>via ExtractBufferLoad]
D --> E{Is reduction buffer<br/>used exactly once?}
E -->|No| REJECT2[Reject: Multiple use]
E -->|Yes| F[Store epilogue_expression_]
F --> G[ScalingDetector<br/>for Mul/Div/Mod]
G --> H{Scaling detected?}
H -->|Yes| REJECT3[Reject: Non-additive scaling]
H -->|No| I[CreateFusedReductionBlock]
I --> J[Init transform:<br/>temp → 0 substitution]
J --> K[Update transform:<br/>GeneralizedEpilogueApplier]
K --> L{Find bias addend<br/>in Add node?}
L -->|Yes| M[Remove bias addend]
L -->|No| N[Apply expression as-is]
M --> O[Fused block completed]
N --> O
style REJECT1 fill:#ffcccc
style REJECT2 fill:#ffcccc
style REJECT3 fill:#ffcccc
style O fill:#ccffcc
0. Terminology
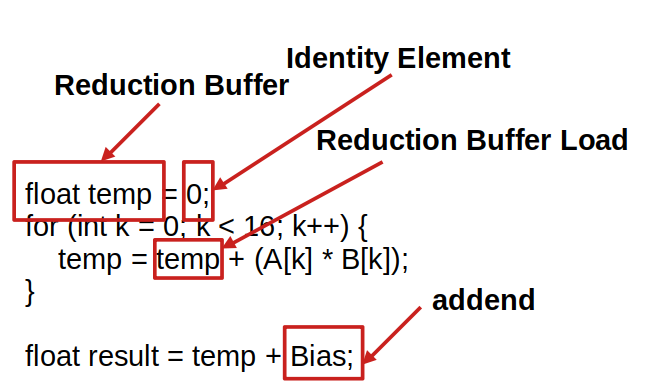
1. Storing the Full Expression
Before:
EpilogueType epilogue_type_;
PrimExpr epilogue_addend_; // Bias-only
PrimExpr clipping_lower_; // Clipping-only
PrimExpr clipping_upper_; // Clipping-only
After:
PrimExpr epilogue_expression_; // Full expression: temp + C, max(temp + C, 0), etc.
const BufferLoadNode* reduction_buffer_load_; // temp[vi, vj] load inside the expression
// Store the epilogue expression and the reduction buffer load
epilogue_expression_ = inlined_store_->value;
reduction_buffer_load_ = loads[0];
2. Init Transformation
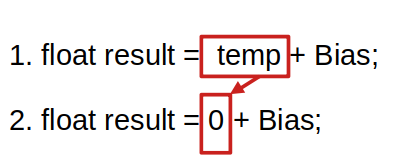
The Init block should compute the epilogue value when the accumulator is the identity element (0 for addition). To achieve this, we replace the reduction buffer load with 0.
class InitSubstituter : public ExprMutator {
PrimExpr VisitExpr_(const BufferLoadNode* op) final {
if (load->buffer.same_as(target_buffer_)) {
return identity_elem_; // temp → 0
}
return ExprMutator::VisitExpr_(op);
}
};
InitSubstituter init_subst(inlined_buffer_, identity_elem);
PrimExpr init_epilogue = init_subst(epilogue_expression_);
// Simplify: 0 + C[vi, vj] → C[vi, vj]
init_epilogue = analyzer.Simplify(init_epilogue);
3. Update Transformation
The Update block should apply the epilogue expression at each iteration, with the reduction buffer load already replaced by the reduction update. At this point, we must handle the addend correctly.
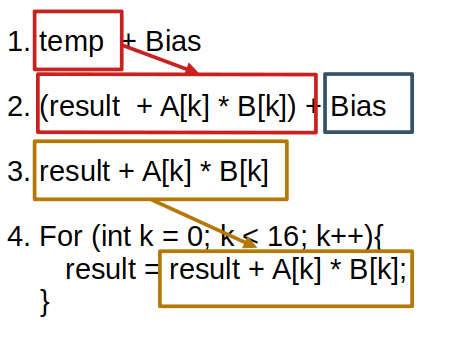
We first replace the reduction buffer load (temp[vi, vj]) with the reduction_update (3. → 4.), and then detect and remove the addend in the Add node (removing the blue rectangle in step 2 of the diagram).
class GeneralizedEpilogueApplier : public ExprMutator {
// 1. Replace reduction buffer load with reduction update
PrimExpr VisitExpr_(const BufferLoadNode* op) final {
if (load->buffer.same_as(target_buffer_)) {
return replacement_; // temp → reduction_update
}
return ExprMutator::VisitExpr_(op);
}
// 2. Automatically detect and remove the addend in Add nodes
PrimExpr VisitExpr_(const AddNode* op) final {
PrimExpr a = VisitExpr(op->a);
bool found_in_a = found_target_load_;
found_target_load_ = false;
PrimExpr b = VisitExpr(op->b);
bool found_in_b = found_target_load_;
if (found_in_a || found_in_b) {
// Check that the other operand does not come from the reduction buffer.
// If so, it is a bias addend that should be removed.
bool other_is_reduction = /* Check if the other operand is from the reduction buffer */;
if (!other_is_reduction) {
// Remove addend
return found_in_a ? a : b;
}
}
return Add(a, b);
}
};
4. Preventing Invalid Fusion
We added validation logic to reject mathematically invalid cases.
Preventing Multiple Uses of the Reduction Result
The reduction result must appear exactly once in the epilogue expression.
if (loads.size() != 1) {
return false; // Reject: (temp + C) * (temp + D) is invalid
}
If the reduction result appears multiple times, replacing each occurrence with the reduction update yields incorrect semantics. For example, (temp + C) * (temp + D) becomes (update + C) * (update + D), which is not equal to (final_sum + C) * (final_sum + D).
Preventing Non-Additive Scaling
We reject epilogues that scale the reduction result using multiplication, division, or modulo.
class ScalingDetector : public ExprVisitor {
void VisitExpr_(const MulNode* op) final {
if (ContainsTarget(op->a) || ContainsTarget(op->b)) {
has_scaling_ = true; // Reject: (temp * 2) + C
}
}
// Similar logic for DivNode and ModNode
};
Series Posts
Language: 한국어 (Korean)
